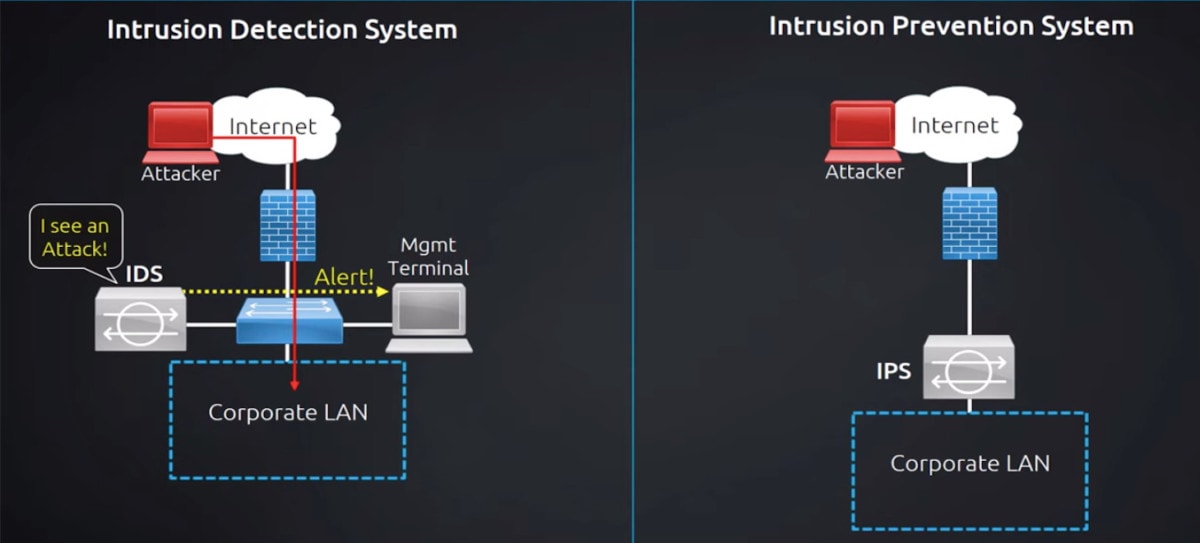
Understanding IDPS:
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are security technologies designed to monitor network and system activities, analyze incoming and outgoing traffic, and detect and respond to security incidents in real-time. These systems employ a combination of signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis techniques to identify suspicious behavior and potential threats.
Key Functionalities of IDPS:
1.Detection: IDPS continuously monitors network traffic and system logs for signs of unauthorized access, malicious activities, or security policy violations. They analyze network packets, application logs, and system events to detect known threats based on predefined signatures and behavior patterns.
2.Prevention: IDPS can take proactive measures to prevent security incidents by blocking or filtering malicious traffic in real-time. They use intrusion prevention techniques, such as packet filtering, protocol validation, and content inspection, to enforce security policies and prevent unauthorized access to network resources.
3.Alerting and Reporting: IDPS generate alerts and reports to notify security administrators about detected security incidents and potential threats. These alerts provide detailed information about the nature of the threat, the affected systems, and recommended remediation actions, enabling timely response and mitigation.
4.Incident Response: IDPS play a crucial role in incident response by providing actionable intelligence and facilitating rapid incident detection, containment, and recovery. They integrate with incident response workflows, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and other security tools to streamline the incident response process.
Importance of IDPS:
1.Proactive Threat Detection: IDPS enable organizations to proactively detect and respond to security threats before they escalate into full-blown security incidents. By continuously monitoring network traffic and system activities, IDPS can identify and mitigate security risks in real-time, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
2.Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, require organizations to implement intrusion detection and prevention controls to protect sensitive data and comply with data protection regulations. IDPS help organizations meet these compliance requirements by providing robust security controls and monitoring capabilities.
3.Protection Against Advanced Threats: In today's threat landscape, traditional security measures alone are insufficient to defend against advanced and sophisticated cyber threats. IDPS leverage advanced detection techniques, such as machine learning, behavioral analysis, and threat intelligence, to identify and mitigate emerging threats that evade traditional security defenses.
4.Reduced Security Incidents: By deploying IDPS, organizations can reduce the frequency and impact of security incidents, minimizing the risk of data breaches, network downtime, and financial losses associated with cyber attacks. IDPS help organizations enhance their overall security posture and resilience against evolving cyber threats.
5.Enhanced Visibility and Control: IDPS provide organizations with enhanced visibility into network activities, user behavior, and security events, enabling better threat detection, incident response, and security policy enforcement. They empower security teams to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect their network infrastructure.
Conclusion:
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are critical components of modern cybersecurity strategies, providing organizations with proactive threat detection, prevention, and incident response capabilities. By deploying IDPS, organizations can enhance their network security posture, mitigate security risks, and comply with regulatory requirements. Investing in robust IDPS solutions is essential for organizations looking to defend against evolving cyber threats and safeguard their sensitive data assets in today's dynamic threat landscape